Data Overview

In a retrospective clinical study of 205 patients:
The HydroMID® showed a statistically significant reduction in failure rates and 6X fewer complications than standard polyurethane.
The HydroMID catheters demonstrated no DVTs versus 7% DVTs with the standard polyurethane catheters.
Taking into account all of the complication costs, the polyurethane catheters incurred an estimated $175,000+ in additional costs for complications with 7 DVTs and 22 device replacements versus the HydroMID devices.**
*Bunch, J. (2022). A Retrospective Assessment of Peripheral Catheter Failures Focusing on Catheter Composition. Journal of Infusion Nursing.
**Cost data on file at Access Vascular Inc.
HydroMID® Study Analysis*
Results of a Bench Model Investigation Bacterial Adhesion:
HBM versus TPU & Fluoro-TPU
-
The purpose of this study was to compare bacterial adhesion on catheter samples using in-vitro blood flow and static models.
-
Fresh heparinized bovine blood was radiolabeled, and bacteria (Staphylococcus Aureus) was introduced.
TPU, Fluoro-modified TPU and HBM catheters were inserted into tubing segments
At the end of the flow phase, the catheters were explanted from the tubing and incubated in vials.
After the 4-hour incubation phase, the thrombus/bacteria were stripped from each catheter, processed and plated to measure the number of bacteria and thrombus present on each catheter.
A total of 12 replications were completed.
-
Conclusion
The data presented demonstrates a strong correlation between relative thrombogenicity and reduced bacterial adhesion of the HBM compared to traditional polyurethane devices.
Reduction of thrombus accumulation was evaluated using in vitro models. Pre-clinical in vitro valuations do not necessarily predict clinical performance with respect to thrombus formation.
LeRoy, K. J., & Donahue, D. T. (2023). Presented at AVA 2023 via e-poster.
Results of a Bench Model Investigation Bacterial Adhesion:
HBM versus TPU & CHG-coated TPU
-
The purpose of this study was to compare bacterial adhesion on catheter samples using in-vitro blood flow and static models.
-
Fresh heparinized bovine blood was radiolabeled, and bacteria (Staphylococcus Aureus) was introduced.
Catheters were conditioned in sterile saline for 72 hours.
TPU, CHG-coated TPU and HBM catheters were inserted into tubing segments
At the end of the flow phase, the catheters were explanted from the tubing and incubated in vials.
After the 4-hour incubation phase, the thrombus/bacteria were stripped from each catheter, processed and plated to measure the number of bacteria and thrombus present on each catheter.
A total of 3 replications were completed.
-
Conclusion
The data presented demonstrates a strong correlation between relative thrombogenicity and reduced bacterial adhesion of the HBM compared to traditional polyurethane devices.
Reduction of thrombus accumulation was evaluated using in vitro models. Pre-clinical in vitro valuations do not necessarily predict clinical performance with respect to thrombus formation.
Korycka, E. (2024). Presented on podium at INS 2024.
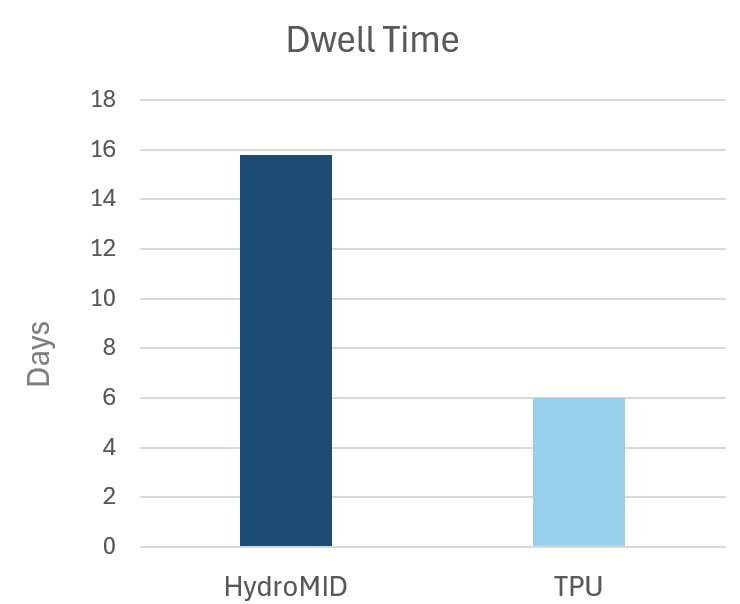
Evaluation of Dwell Time of Hydrophilic Biomaterial Midline Catheters
In an evaluation in outcomes of the HydroMID in a study of 29 patients, the mean dwell time was 15.8 days. There were no incidences of phlebitis, occlusion, DVT, or BSI reported. Read the full study results below
Data in this study was not comparative but represents published dwell time for standard TPU catheters. Read the whitepaper for details.
Three 4 Fr PICC devices that were evaluated in the in vitro trackability and pushability test.
HydroPICC® reduced the average tracking force vs a standard polyurethane catheter by 84%.
HydroPICC reduced the average tracking force vs a thromboresistant polyurethane catheter by 90%.
Trackability Comparison
HydroPICC® Study Details
In a retrospective clinical study of 121 patients:
The HydroPICC demonstrated no occlusions or replacements compared to 13 occlusions and 8 replacements with the standard polyurethane catheter.
Using HydroPICC resulted in a potential savings of up to 50% in additional material costs versus the standard polyurethane catheter highlighting the potential for time and cost savings with this device.
**Bunch, J. (2023). A retrospective, comparative, clinical study of occlusion rate of peripherally inserted central catheters fabricated of poly(vinyl alcohol)-based hydrogel composite. Journal of Materials Science: Materials Science in Medicine (2023) 34:34.
Are you interested in learning more about our products?